Immunity and Immune response
We do not know about the many beautiful things in the world
that are interesting and fundamental. In this article, we will learn about the
body’s defense mechanism.
 |
| Immunity and Immune Response |
There are different types of immune systems to protect the
human body, just like the defense systems to protect the people of a country.
For a country’s overall security, police, army, navy, and intelligence officers
work collectively. Similarly, for the overall safety of a person against
diseases, many units collectively work as the defense system, which is called
the immune system. Therefore, the human body’s immune system is a system that
ensures that no disease germs can enter the body and make the body sick. If the
germs outside are strong, a person with weak immunity may get sick. For instance,
If a criminal has a powerful weapon than the anti-crime force, the criminal may
win.
Therefore, To stay healthy, the immune system must be active.
A person’s immune system helps to protect him from all kinds
of diseases. When a germ invades the human body, the immune system works in
different ways to inhibit the microbe and keep us safe. The immune system forms
these ways that inhibit germs. The immune response can be stronger or weaker
depending on genetic makeup, lifestyle, or eating habits. People can stay
healthy if their immunity is strong.
Classification
White blood cells
play a vital role in immunity, so it is crucial to know blood cell formation.
The stem cells produce the first two types of cells through hematopoiesis in
the human body.
- Myeloid Progenitor
- Lymphoid Progenitor
Myeloid generates the
following cells
- Megakaryocyte that makes platelets,
- Erythrocyte that produces red blood cells
- Mast cell
- Myeloblast generates neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils,
monocyte. Monocytes generate macrophages.
The lymphoid produces two types of cells. They are
- The
killer cells, and - The lymphocytes.
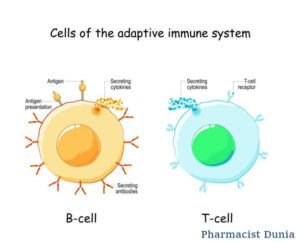
T cells and B cells form from Lymphocytes. Plasma cells
generate from B cells. And all these cells play a vital role in immunity.
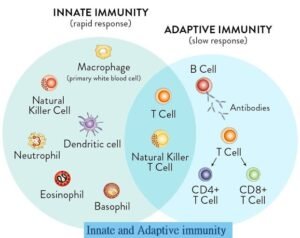
There are usually two types of immune systems.
- Innate immunity
- Adaptive immunity
- Innate immunity
- Adaptive immunity
Innate immunity
Innate immunity tends to be a lot more genetic. It is also
called first-line and second-line immunity.
Innate immunity is nonspecific, meaning that if the virus or
bacterium, or microbe affects the body, it will destroy all the microbes in a
single mechanism of action. It gives natural immunity and life-long protection
to a person.
This immunity is of
two types.
- External Innate Immunity
- Internal Innate Immunity
External Innate Immunity
External Innate Immunity is called the first-line of defense
mechanism. It prevents germs from entering the body using a variety of ways.
1. The keratin layer
of the skin prevents germs from entering the skin.
2. Dust and various
pathogens cannot enter the lungs for the Miucociliary Movement.
3. Reflexes cause
many germs to excrete through sneezing and coughing.
4. The water in the
eyes contains an enzyme called lysozyme that can destroy germs.
Internal Innate Immunity
Internal Innate Immunity is of two types.
- Humoral
- Cellular
Humoral:
Humoral immunity naturally resists disease inside the body.
For example,
Stomach acid destroys many disease germs.
Bacteria of the intestine
Complement system
Interferon
The complement system is produced from the liver and
circulates in the blood as inactive. The complement system is activated when a
foreign particle or microbe attacks the body. Approximately fifty types of
proteins and rupture proteins are involved in this system. It helps to kill
many kinds of microbes through Phagocytosis and Inflammation process.
Cellular:
Different types of cells work to destroy pathogenic microbes
such as Macrophages, eosinophils, natural killer cells.
Macrophages:
Macrophage is made up of monocytes and can detect many kinds
of pathogens. It can destroy microbe by phagocytosis, stimulate cytokine to
inhibit pathogens in combination with T cells resulting in inflammation. It
functions in different ways in different types of organs. Various types of
macrophage releasing organs include Alveolar, Kufar cells, Micro swallow,
Splenic.
Eosinophil
Eosinophil plays a vital role in immunity. When a foreign
particle enters the body, it helps to destroy germs by releasing reactive
oxygen such as hypobromide, superoxide, and peroxide.
Killer cell
When a microbe enters the body, it attacks and destroys a
cell. Then the killer cell releases cytokines and inhibits the infected cell
through lysis.
General Mechanism of Innate Immunity
- Prevent microbes from entering the body through physical
barriers like skin and tears.
- When a foreign particle enters the body, it raises the body
temperature causing fever. This increased body heat stimulates the phagocytosis
process that inhibits the microbes.
- Inhibit the growth of different types of microbes inside the
body
- Activate the complement system.
- When the microbe attacks the cell, the infected cell
releases interferon. Interferon helps to
activate the antimicrobial activity of the surrounding cells.
- The glands in the body destroy microbes releasing
antibacterial enzymes like lactoferrin.
- Antimicrobial enzymes inhibit microbes such as lysozyme.
- Body Destroys germs through phagocytosis. Macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils,
basophils are common phagocytes.
2. Adaptive immunity
When the body
acquires immunity for a particular disease, it is called adaptive immunity.
Adaptive immunity is specific and is not achieved by birth. It produces
specific immune responses on specific pathogens. When the bacteria invade, it inhibits the
bacteria in one way, while when the virus attacks, it inhibits it in another
way.
Adaptive immunity is acquired by vaccination. It is also called the body’s third line of
defense mechanism. B cells and T cells play a vital role.
There are two types
of adaptive immunity
- Active adaptive immunity
- Passive adaptive immunity
Active adaptive
immunity
Active adaptive
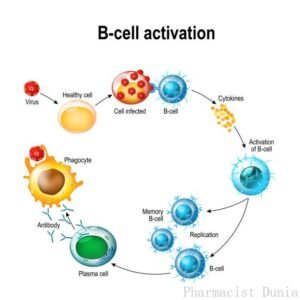
immunity is achieved in two ways. When a
microbe captures the body, the body produces antibodies and B cell memory. Later this memory and antibodies destroy this
microbe. As long as the body can retain
memory, the germs can no longer cause the disease in the body. Such as chickenpox.
A vaccine may protect
the body before a specific germ attack, such as polio.
Passive adaptive immunity
When a person gets immunity from someone, it is called
passive immunity.
Such as a baby
acquire from its mother through breast milk and placenta.
Corona patients are diagnosed with such plasma therapy. After the corona is infected, The patient’s
immune response is activated, and it generates antibodies. The patient having
active antibodies can survive. These
antibodies are used to diagnose another patient through plasma.
Mechanism of adaptive
immunity
Humoral immunity
mechanism
When the germs of a
disease enters the body and circulates in the blood, the B cell combines with the
helper T cells to make antibodies that only work for that particular germ,
making specific antibodies for a determined pathogen. These antibodies destroy
that germ only.
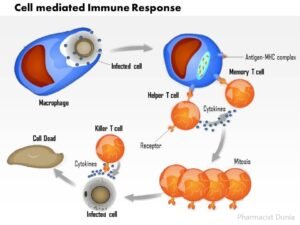
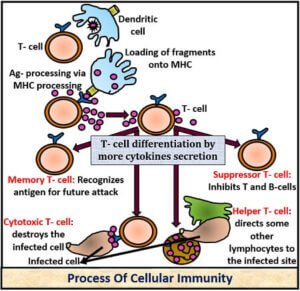
Cellular immunity
mechanism
In this mechanism,
the cell infected by the germ is inhibited. But the immune system makes sure
that the healthy cells in the vicinity are safe. When a microbe attacks a cell, the helper T
cell releases the cytokine. The activated T cell arrives at the spot and
inhibits the cell infected by the microbe.